Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
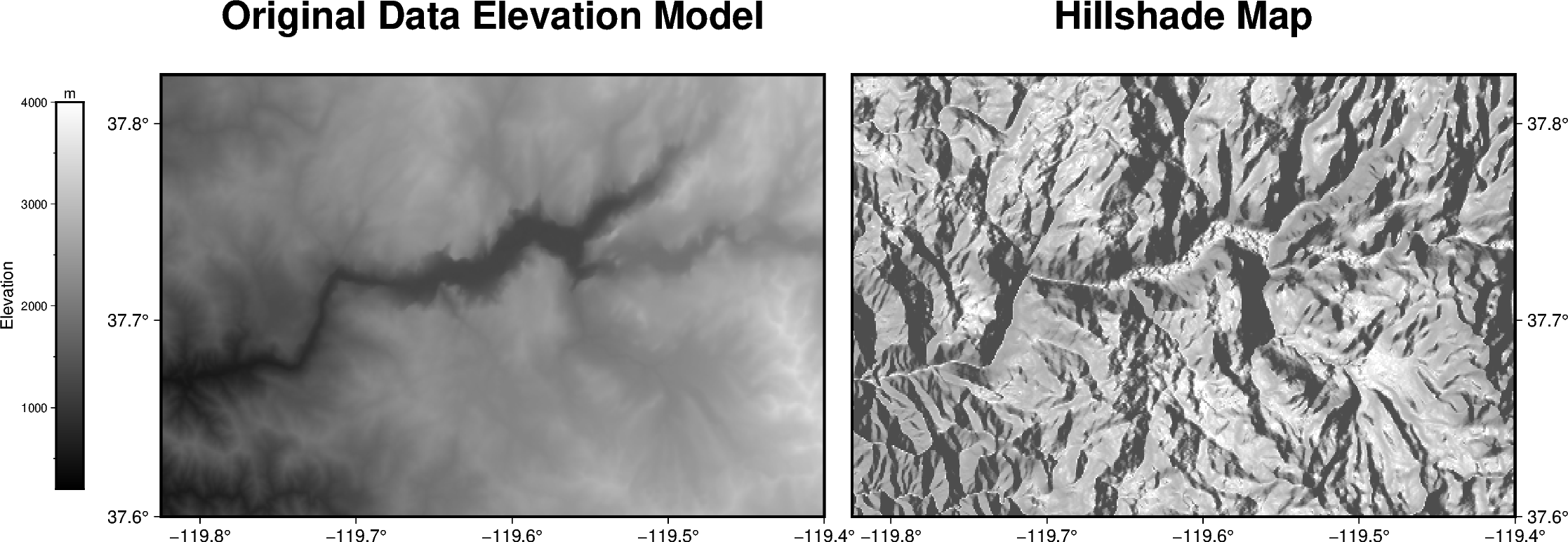
Calculating grid gradient and radiance
The pygmt.grdgradient function calculates the gradient of a grid file.
In the example shown below we will see how to calculate a hillshade map based
on a Data Elevation Model (DEM). As input pygmt.grdgradient gets
an xarray.DataArray object or a path string to a grid file, calculates
the respective gradient and returns it as an xarray.DataArray object.
We will use the radiance parameter in order to set the illumination source
direction and altitude.
import pygmt
# Define region of interest around Yosemite valley
region = [-119.825, -119.4, 37.6, 37.825]
# Load sample grid (3 arc-seconds global relief) in target area
grid = pygmt.datasets.load_earth_relief(resolution="03s", region=region)
# calculate the reflection of a light source projecting from west to east
# (azimuth of 270 degrees) and at a latitude of 30 degrees from the horizon
dgrid = pygmt.grdgradient(grid=grid, radiance=[270, 30])
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# define figure configuration
pygmt.config(FORMAT_GEO_MAP="ddd.x", MAP_FRAME_TYPE="plain")
# --------------- plotting the original Data Elevation Model -----------
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="gray", series=[200, 4000, 10])
fig.grdimage(
grid=grid,
projection="M12c",
frame=["WSrt+tOriginal Data Elevation Model", "xa0.1", "ya0.1"],
cmap=True,
)
fig.colorbar(position="JML+o1.4c/0c+w7c/0.5c", frame=["xa1000f500+lElevation", "y+lm"])
# --------------- plotting the hillshade map -----------
# Shift plot origin of the second map by 12.5 cm in x direction
fig.shift_origin(xshift="12.5c")
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="gray", series=[-1.5, 0.3, 0.01])
fig.grdimage(
grid=dgrid,
projection="M12c",
frame=["lSEt+tHillshade Map", "xa0.1", "ya0.1"],
cmap=True,
)
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.393 seconds)