Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
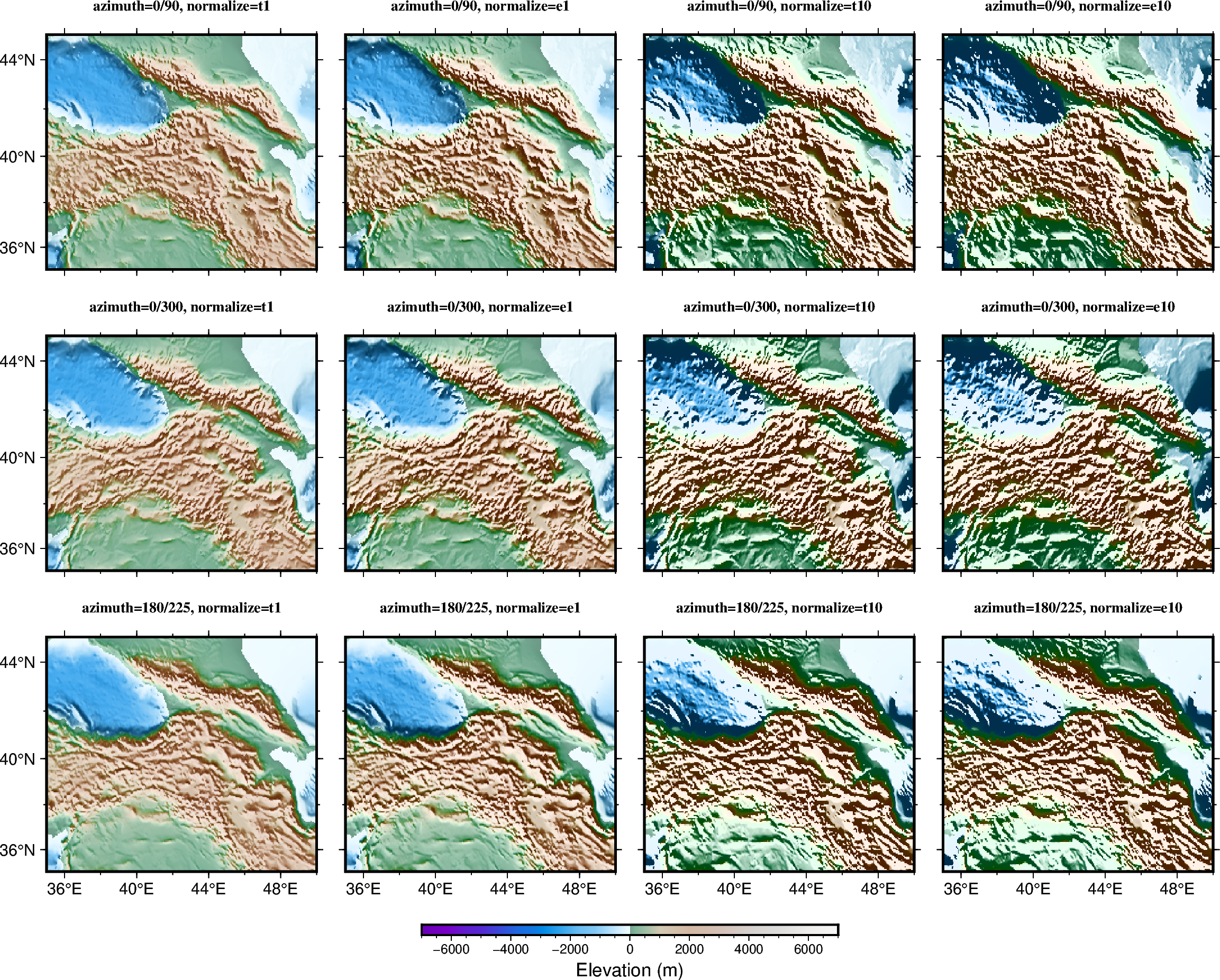
Calculating grid gradient with custom azimuth and normalize parameters
The pygmt.grdgradient function calculates the gradient of a grid file.
As input, pygmt.grdgradient gets an xarray.DataArray object
or a path string to a grid file. It then calculates the respective gradient
and returns an xarray.DataArray object. The example below sets two
main parameters:
azimuthto set the illumination light source direction (0° is North, 90° is East, 180° is South, 270° is West).normalizeto enhance the three-dimensional sense of the topography.
The normalize parameter calculates the azimuthal gradient of each point
along a certain azimuth angle, then adjusts the brightness value of the color
according to the positive/negative of the azimuthal gradient and the amplitude
of each point.
grdblend [NOTICE]: Remote data courtesy of GMT data server oceania [http://oceania.generic-mapping-tools.org]
grdblend [NOTICE]: SRTM15 Earth Relief v2.6 at 03x03 arc minutes reduced by Gaussian Cartesian filtering (15.7 km fullwidth) [Tozer et al., 2019].
grdblend [NOTICE]: -> Download 90x90 degree grid tile (earth_relief_03m_g): N00E000
import pygmt
# Load the 3 arc-minutes global relief grid in the target area around Caucasus
grid = pygmt.datasets.load_earth_relief(resolution="03m", region=[35, 50, 35, 45])
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# Define a colormap to be used for topography
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="terra", series=[-7000, 7000])
# Define figure configuration
pygmt.config(FONT_TITLE="10p,5", MAP_TITLE_OFFSET="1p", MAP_FRAME_TYPE="plain")
# Setup subplot panels with three rows and four columns
with fig.subplot(
nrows=3,
ncols=4,
figsize=("28c", "21c"),
sharex="b",
sharey="l",
):
# E.g. "0/90" illuminates light source from the North (top) and East
# (right), and so on
for azi in ["0/90", "0/300", "180/225"]:
# "e" and "t" are cumulative Laplace distribution and cumulative
# Cauchy distribution, respectively
# "amp" (e.g. 1 or 10) controls the brightness value of the color
for nor in ["t1", "e1", "t10", "e10"]:
# Making an intensity DataArray using azimuth and normalize
# parameters
shade = pygmt.grdgradient(grid=grid, azimuth=azi, normalize=nor)
fig.grdimage(
grid=grid,
shading=shade,
projection="M?",
frame=["a4f2", f"+tazimuth={azi}, normalize={nor}"],
cmap=True,
panel=True,
)
fig.colorbar(position="JBC+w10c/0.25c+h", frame="xa2000f500+lElevation (m)")
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.499 seconds)