pygmt.Figure.coast
- Figure.coast(*, area_thresh=None, frame=None, lakes=None, resolution=None, dcw=None, box=None, land=None, rivers=None, projection=None, map_scale=None, borders=None, region=None, water=None, verbose=None, shorelines=None, panel=None, perspective=None, transparency=None, **kwargs)
Plot continents, countries, shorelines, rivers, and borders.
Plots grayshaded, colored, or textured land masses [or water masses] on maps and [optionally] draws coastlines, rivers, and political boundaries. The data files come in 5 different resolutions: (f)ull, (h)igh, (i)ntermediate, (l)ow, and (c)rude. The full resolution files amount to more than 55 Mb of data and provide great detail; for maps of larger geographical extent it is more economical to use one of the other resolutions. If the user selects to paint the land areas and does not specify fill of water areas then the latter will be transparent (i.e., earlier graphics drawn in those areas will not be overwritten). Likewise, if the water areas are painted and no land fill is set then the land areas will be transparent.
A map projection must be supplied.
Full option list at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.5/coast.html
Aliases:
A = area_thresh
B = frame
C = lakes
D = resolution
E = dcw
F = box
G = land
I = rivers
J = projection
L = map_scale
N = borders
R = region
S = water
V = verbose
W = shorelines
c = panel
p = perspective
t = transparency
- Parameters:
projection (str) – projcode[projparams/]width|scale. Select map projection.
region (str or list) – xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax[+r][+uunit]. Specify the region of interest. Required if this is the first plot command.
area_thresh (float or str) – min_area[/min_level/max_level][+a[g|i][s|S]][+l|r][+ppercent]. Features with an area smaller than min_area in km2 or of hierarchical level that is lower than min_level or higher than max_level will not be plotted [Default is
"0/0/4"(all features)].frame (bool, str, or list) – Set map boundary frame and axes attributes.
lakes (str or list) – fill[+l|+r]. Set the shade, color, or pattern for lakes and river-lakes. The default is the fill chosen for “wet” areas set by the
waterparameter. Optionally, specify separate fills by appending +l for lakes or +r for river-lakes, and passing multiple strings in a list.resolution (str) – f|h|i|l|c. Select the resolution of the data set to: (f)ull, (h)igh, (i)ntermediate, (l)ow, and (c)rude.
land (str) – Select filling of “dry” areas.
river[/pen]. Draw rivers. Specify the type of rivers and [optionally] append pen attributes [Default is
"0.25p,black,solid"].Choose from the list of river types below; pass a list to
riversto use multiple arguments.0: double-lined rivers (river-lakes)1: permanent major rivers2: additional major rivers3: additional rivers4: minor rivers5: intermittent rivers - major6: intermittent rivers - additional7: intermittent rivers - minor8: major canals9: minor canals10: irrigation canals
You can also choose from several preconfigured river groups:
"a": rivers and canals (0-10)"A": rivers and canals except river-lakes (1-10)"r": permanent rivers (0-4)"R": permanent rivers except river-lakes (1-4)"i": intermittent rivers (5-7)"c": canals (8-10)
map_scale (str) – [g|j|J|n|x]refpoint+wlength. Draw a simple map scale centered on the reference point specified.
box (bool or str) – [+cclearances][+gfill][+i[[gap/]pen]][+p[pen]][+r[radius]][+s[[dx/dy/][shade]]]. If set to
True, draw a rectangular border around the map scale or rose. Alternatively, specify a different pen with +ppen. Add +gfill to fill the scale panel [Default is no fill]. Append +cclearance where clearance is either gap, xgap/ygap, or lgap/rgap/bgap/tgap where these items are uniform, separate in x- and y-direction, or individual side spacings between scale and border. Append +i to draw a secondary, inner border as well. We use a uniform gap between borders of 2p and the MAP_DEFAULTS_PEN unless other values are specified. Append +r to draw rounded rectangular borders instead, with a 6p corner radius. You can override this radius by appending another value. Finally, append +s to draw an offset background shaded region. Here, dx/dy indicates the shift relative to the foreground frame [Default is"4p/-4p"] and shade sets the fill style to use for shading [Default is"gray50"].border[/pen]. Draw political boundaries. Specify the type of boundary and [optionally] append pen attributes [Default is
"0.25p,black,solid"].Choose from the list of boundaries below. Pass a list to
bordersto use multiple arguments.1: national boundaries2: state boundaries within the Americas3: marine boundaries"a": all boundaries (1-3)
water (str) – Select filling “wet” areas.
shorelines (int, str, or list) – [level/]pen. Draw shorelines [Default is no shorelines]. Append pen attributes [Default is
"0.25p,black,solid"] which apply to all four levels. To set the pen for a single level, pass a string with level/pen, where level is 1-4 and represent coastline, lakeshore, island-in-lake shore, and lake-in-island-in-lake shore. Pass a list of level/pen strings toshorelinesto set multiple levels. When specific level pens are set, those not listed will not be drawn.dcw (str or list) – code1,code2,…[+gfill][+ppen][+z]. Select painting country polygons from the Digital Chart of the World. Append one or more comma-separated countries using the 2-character ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 convention. To select a state of a country (if available), append .state, (e.g,
"US.TX"for Texas). To specify a whole continent, prepend = to any of the continent codes (e.g."=EU"for Europe). Append +ppen to draw polygon outlines [Default is no outline] and +gfill to fill them [Default is no fill].Select a specific subplot panel. Only allowed when used in
Figure.subplotmode.Trueto advance to the next panel in the selected order.index to specify the index of the desired panel.
(row, col) to specify the row and column of the desired panel.
The panel order is determined by the
Figure.subplotmethod. row, col and index all start at 0.perspective (list or str) – [x|y|z]azim[/elev[/zlevel]][+wlon0/lat0[/z0]][+vx0/y0]. Select perspective view and set the azimuth and elevation angle of the viewpoint [Default is
[180, 90]]. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.5/gmt.html#perspective-full.transparency (float) – Set transparency level, in [0-100] percent range [Default is
0, i.e., opaque]. Only visible when PDF or raster format output is selected. Only the PNG format selection adds a transparency layer in the image (for further processing).verbose (bool or str) – Select verbosity level [Full usage].
Example
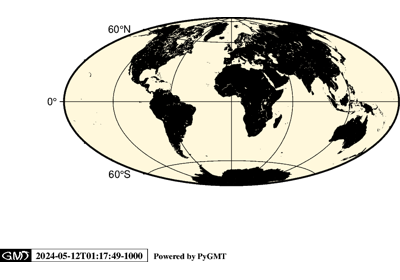
>>> import pygmt >>> # Create a new plot with pygmt.Figure() >>> fig = pygmt.Figure() >>> # Call the coast method for the plot >>> fig.coast( ... # Set the projection to Mercator, and the plot width to 10 centimeters ... projection="M10c", ... # Set the region of the plot ... region=[-10, 30, 30, 60], ... # Set the frame of the plot, here annotations and major ticks ... frame="a", ... # Set the color of the land to "darkgreen" ... land="darkgreen", ... # Set the color of the water to "lightblue" ... water="lightblue", ... # Draw national borders with a 1-point black line ... borders="1/1p,black", ... ) >>> # Show the plot >>> fig.show()
Examples using pygmt.Figure.coast
GeoPandas: Plotting lines with LineString or MultiLineString geometry