Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Choropleth map
The pygmt.Figure.plot method allows us to plot geographical data such
as polygons which are stored in a geopandas.GeoDataFrame object. Use
geopandas.read_file to load data from any supported OGR format such as
a shapefile (.shp), GeoJSON (.geojson), geopackage (.gpkg), etc. You can also
use a full URL pointing to your desired data source. Then, pass the
geopandas.GeoDataFrame as an argument to the data parameter of
pygmt.Figure.plot, and style the geometry using the pen parameter.
To fill the polygons based on a corresponding column you need to set
fill="+z" as well as select the appropriate column using the aspatial
parameter as shown in the example below.
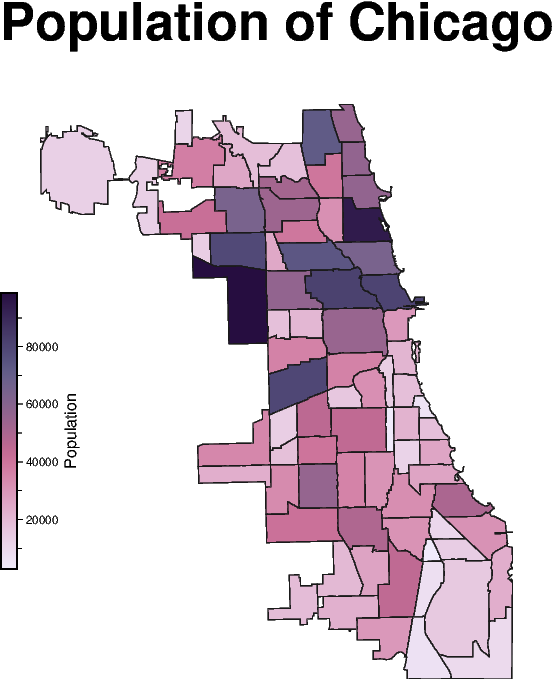
import geopandas as gpd
import pygmt
# Read polygon data using geopandas
gdf = gpd.read_file("https://geodacenter.github.io/data-and-lab/data/airbnb.zip")
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(
region=gdf.total_bounds[[0, 2, 1, 3]],
projection="M6c",
frame="+tPopulation of Chicago",
)
# The dataset contains different attributes, here we select
# the "population" column to plot.
# First, we define the colormap to fill the polygons based on
# the "population" column.
pygmt.makecpt(
cmap="acton",
series=[gdf["population"].min(), gdf["population"].max(), 10],
continuous=True,
reverse=True,
)
# Next, we plot the polygons and fill them using the defined colormap.
# The target column is defined by the aspatial parameter.
fig.plot(
data=gdf,
pen="0.3p,gray10",
fill="+z",
cmap=True,
aspatial="Z=population",
)
# Add colorbar legend
fig.colorbar(frame="x+lPopulation", position="jML+o-0.5c+w3.5c/0.2c")
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.738 seconds)