Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
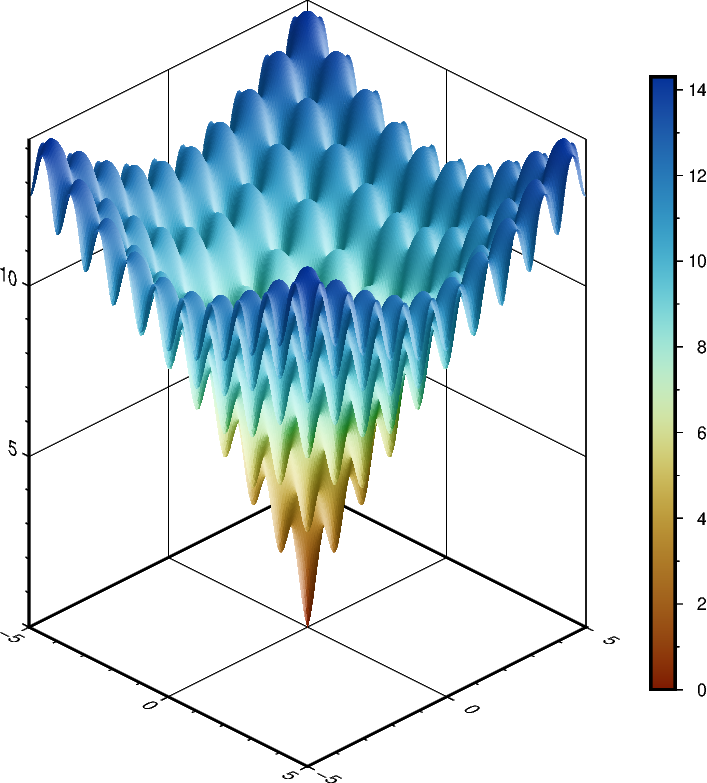
Plotting a surface
The pygmt.Figure.grdview method can plot 3-D surfaces with
surftype="s". Here, we supply the data as an xarray.DataArray with
the coordinate vectors x and y defined. Note that the perspective
parameter here controls the azimuth and elevation angle of the view. We provide
a list of two arguments to frame - the first argument specifies the
\(x\)- and \(y\)-axes frame attributes and the second argument,
prepended with "z", specifies the \(z\)-axis frame attributes.
Specifying the same scale for the projection and zscale parameters
ensures equal axis scaling. The shading parameter specifies illumination;
here we choose an azimuth of 45° with shading="+a45".
import numpy as np
import pygmt
import xarray as xr
# Define an interesting function of two variables, see:
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ackley_function
def ackley(x, y):
"""
Ackley function.
"""
return (
-20 * np.exp(-0.2 * np.sqrt(0.5 * (x**2 + y**2)))
- np.exp(0.5 * (np.cos(2 * np.pi * x) + np.cos(2 * np.pi * y)))
+ np.exp(1)
+ 20
)
# Create gridded data
INC = 0.05
x = np.arange(-5, 5 + INC, INC)
y = np.arange(-5, 5 + INC, INC)
data = xr.DataArray(ackley(*np.meshgrid(x, y)), coords=(x, y))
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# Plot grid as a 3-D surface
SCALE = 0.5 # in centimeters
fig.grdview(
data,
# Set annotations and gridlines in steps of five, and
# tick marks in steps of one
frame=["a5f1g5", "za5f1g5"],
projection=f"x{SCALE}c",
zscale=f"{SCALE}c",
surftype="s",
cmap="roma",
perspective=[135, 30], # Azimuth southeast (135°), at elevation 30°
shading="+a45",
)
# Add colorbar for gridded data
fig.colorbar(
frame="a2f1", # Set annotations in steps of two, tick marks in steps of one
position="JRM", # Place colorbar at position Right Middle
)
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.305 seconds)