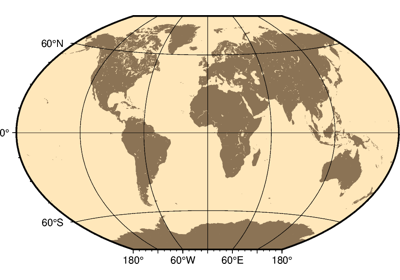
Projections
PyGMT supports many map projections. Use the projection parameter to specify which
one you want to use in all plotting methods. The projection is specified by a one-letter
code along with (sometimes optional) reference longitude and latitude and the
width of the map (for example, Alon0/lat0[/horizon]/width). The map
height is determined based on the region and projection.
These are all the available projections:
Azimuthal Projections
Conic Projections
Cylindric Projections
Miscellaneous Projections
Non-geographic Projections
Projection Table
The table below shows the projection codes for the 31 GMT projections:
PyGMT Projection Argument |
Projection Name |
|---|---|
Alon0/lat0[/horizon]/width |
|
Blon0/lat0/lat1/lat2/width |
|
Clon0/lat0/width |
|
Cyl_stere/[lon0/[lat0/]]width |
|
Dlon0/lat0/lat1/lat2/width |
|
Elon0/lat0[/horizon]/width |
|
Flon0/lat0[/horizon]/width |
|
Glon0/lat0[/horizon]/width |
|
Glon0/lat0/width[+aazimuth][+ttilt][+vvwidth/vheight][+wtwist][+zaltitude] |
|
H[lon0/]width |
|
I[lon0/]width |
|
J[lon0/]width |
|
Kf[lon0/]width |
|
Ks[lon0/]width |
|
Llon0/lat0/lat1/lat2/width |
|
M[lon0/[lat0/]]width |
|
N[lon0/]width |
|
Oalon0/lat0/azimuth/width[+v] |
|
Oblon0/lat0/lon1/lat1/width[+v] |
|
Oclon0/lat0/lonp/latp/width[+v] |
|
Pwidth[+a][+f[e|p|radius]][+roffset][+torigin][+z[p|radius]] |
Polar [azimuthal] (\(\theta, r\)) (or cylindrical) |
Poly/[lon0/[lat0/]]width |
|
Q[lon0/[lat0/]]width |
|
R[lon0/]width |
|
Slon0/lat0[/horizon]/width |
|
Tlon0[/lat0]/width |
|
Uzone/width |
|
V[lon0/]width |
|
W[lon0/]width |
|
Xwidth[l|pexp|T|t][/height[l|pexp|T|t]][d] |
Linear, logarithmic, power, and time |
Ylon0/lat0/width |