pygmt.Figure.solar
- Figure.solar(terminator='d', terminator_datetime=None, *, frame=None, fill=None, projection=None, region=None, verbose=None, pen=None, panel=None, perspective=None, transparency=None, **kwargs)
Plot day-light terminators or twilights.
This function plots the day-night terminator. Alternatively, it can plot the terminators for civil twilight, nautical twilight, or astronomical twilight.
Full option list at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/solar.html
Aliases:
B = frame
G = fill
J = projection
R = region
V = verbose
W = pen
c = panel
p = perspective
t = transparency
- Parameters
terminator (str) –
Set the type of terminator displayed. Valid arguments are
"day_night","civil","nautical", and"astronomical", which can be set with either the full name or the first letter of the name [Default is"day_night"].Refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Twilight for the definitions of different types of twilight.
terminator_datetime (str or datetime object) – Set the UTC date and time of the displayed terminator [Default is the current UTC date and time]. It can be passed as a string or Python datetime object.
region (str or list) – xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax[+r][+uunit]. Specify the region of interest.
projection (str) – projcode[projparams/]width. Select map projection.
frame (bool or str or list) – Set map boundary frame and axes attributes.
fill (str) – Set color or pattern for filling terminators [Default is no fill].
pen (str) – Set pen attributes for lines [Default is
"0.25p,black,solid"].Select verbosity level [Default is w], which modulates the messages written to stderr. Choose among 7 levels of verbosity:
q - Quiet, not even fatal error messages are produced
e - Error messages only
w - Warnings [Default]
t - Timings (report runtimes for time-intensive algorithms)
i - Informational messages (same as
verbose=True)c - Compatibility warnings
d - Debugging messages
panel (bool or int or list) – [row,col|index]. Select a specific subplot panel. Only allowed when in subplot mode. Use
panel=Trueto advance to the next panel in the selected order. Instead of row,col you may also give a scalar value index which depends on the order you set viaautolabelwhen the subplot was defined. Note: row, col, and index all start at 0.perspective (list or str) – [x|y|z]azim[/elev[/zlevel]][+wlon0/lat0[/z0]][+vx0/y0]. Select perspective view and set the azimuth and elevation angle of the viewpoint [Default is
[180, 90]]. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/gmt.html#perspective-full.transparency (int or float) – Set transparency level, in [0-100] percent range [Default is
0, i.e., opaque]. Only visible when PDF or raster format output is selected. Only the PNG format selection adds a transparency layer in the image (for further processing).
Example
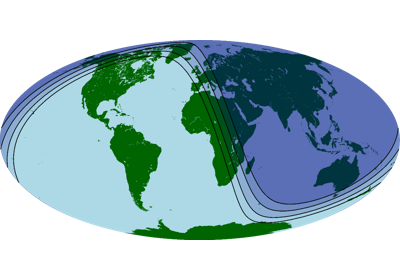
>>> # import the Python module "datetime" >>> import datetime >>> import pygmt >>> # create a datetime object at 8:52:18 on June 24, 1997 (time in UTC) >>> date = datetime.datetime( ... year=1997, month=6, day=24, hour=8, minute=52, second=18 ... ) >>> # create a new plot with pygmt.Figure() >>> fig = pygmt.Figure() >>> # create a map of the Earth with the coast method >>> fig.coast( ... land="darkgreen", water="lightblue", projection="W10c", region="d" ... ) >>> fig.solar( ... # set the terminator to "day_night" ... terminator="day_night", ... # pass the datetime object ... terminator_datetime=date, ... # fill the night-section with navyblue at 75% transparency ... fill="navyblue@75", ... # draw the terminator with a 1-point black line ... pen="1p,black", ... ) >>> # show the plot >>> fig.show()